This week's module broadly examines
EMR and its significance in Remote Sensing (how reflection, refraction, scattering, absorption, etc. impact remote sensing technologies). This week's lab is separated into three exercises aimed at examining the properties of electromagnetic radiation and introducing
ERDAS Imagine (an analytical tool used in remote sensing in conjunction with other GIS products). (
Here is a brief overview by the Office of Surface Mining of Imagine with links to PDF directions). The first exercise concentrates solely on calculations of wavelength, frequency, and photon energy (C = λν and Q = hν) to look at the
particle and
wave theories of light. The second exercise focuses on understanding the graphic use interface of Imagine as well as manipulating parameters and exploring various types of raster data. The final exercise prepares data in Imagine and exports it for map making in ArcGIS.
This third exercise produces the sole cartographic output of the module. To complete this portion I used a classified raster image of Washington State and randomly chose a section (using the
Inquire Box tool) to analyze. I also added an Area column to the attribute table. This area data was then incorporated into the legend made in ArcGIS. Imagine has some tricky aspects to it but the layout somewhat resembles that of the GUI of ArcMap. Thus, some tasks seemed intuitive (like right clicking a layer in the
Contents panel and editing the attribute table). The Help for this program is also similar to ArcGIS and easy to navigate.
I included my map below showing the random subset of forest land I selected. The legend shows the seven raster classifications with their concomitant areas in hectares.
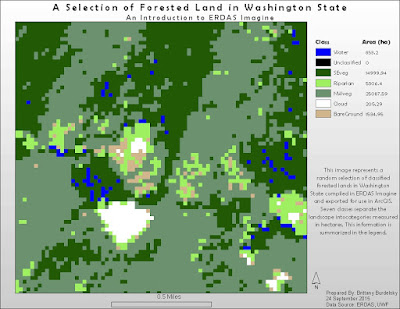 |
| Map 1: A Map Exercise Using a Classified Forest Land Raster of Washington State. |